Exploring Immunotherapy: Revolutionizing Cancer Treatment
Cancer continues to be one of the most formidable challenges in global healthcare, affecting millions of lives and causing immense suffering. Traditional cancer treatments, such as chemotherapy and radiation therapy, have made significant strides, but they often come with debilitating side effects and limited efficacy. In recent years, however, a groundbreaking approach has emerged, offering new hope and transforming the landscape of cancer treatment: immunotherapy. This innovative field harnesses the power of the immune system to combat cancer, revolutionizing the way we understand and approach this complex disease.
Advancements in Immunotherapy
Success stories and remarkable outcomes of immunotherapy:
Immunotherapy has demonstrated remarkable success stories, offering renewed hope to patients who were once faced with limited treatment options. Numerous cases have shown unprecedented responses and even complete remission in patients with advanced or previously untreatable cancers. For instance, immunotherapy has proven highly effective in treating melanoma, with patients experiencing long-term survival rates that were once considered unattainable. Additionally, immunotherapy has shown promising results in other cancer types such as lung cancer, lymphoma, and bladder cancer. These success stories highlight the transformative potential of immunotherapy, inspiring both patients and healthcare professionals alike.
Clinical trials and research contributing to the advancement of immunotherapy:
Extensive clinical trials and rigorous research efforts have been instrumental in driving the advancements in immunotherapy. Researchers are continuously exploring new immunotherapeutic approaches, optimizing treatment protocols, and uncovering novel targets within the immune system. These trials not only evaluate the safety and efficacy of immunotherapies but also provide valuable insights into their mechanisms of action and potential side effects. By collecting data and analyzing outcomes, researchers are constantly refining and improving immunotherapy techniques, leading to breakthroughs that have significantly expanded treatment options for cancer patients.
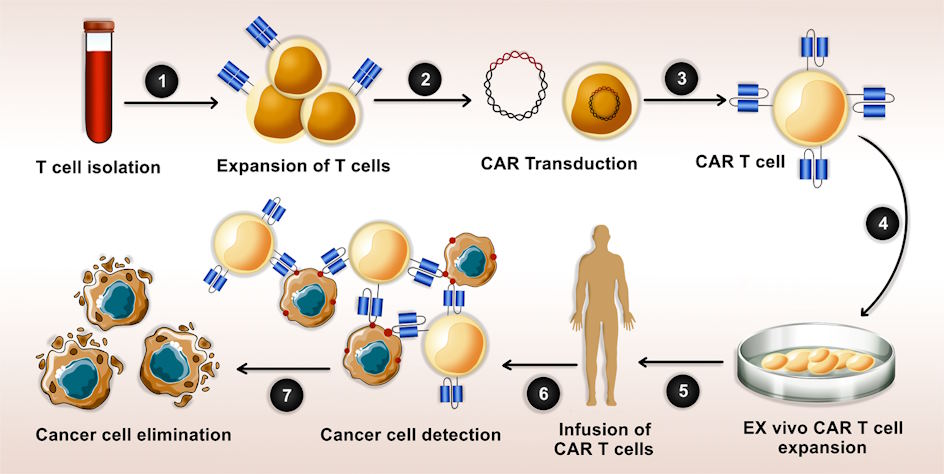
Combination therapies: synergistic effects of combining immunotherapy with other treatments:
Combining immunotherapy with other treatment modalities, such as chemotherapy, targeted therapies, or radiation therapy, has shown promising synergistic effects. The rationale behind combination therapy is to enhance the immune response while simultaneously targeting cancer cells through different mechanisms. For example, certain chemotherapeutic agents have been found to increase the visibility of cancer cells to the immune system, making them more susceptible to immunotherapy. The use of combination therapies has resulted in improved response rates and prolonged survival in various cancers, including melanoma and lung cancer. As researchers continue to explore and optimize these combinations, the potential for even greater treatment efficacy is on the horizon.
Targeted therapies and personalized medicine in immunotherapy:
Immunotherapy has also paved the way for targeted therapies and personalized medicine approaches. By identifying specific molecular targets on cancer cells, researchers have developed therapies that directly address the underlying genetic abnormalities driving tumor growth. This targeted approach allows for more precise and effective treatment, minimizing damage to healthy cells. Additionally, personalized medicine aims to tailor immunotherapy treatments to an individual’s unique genetic and immune profile, maximizing treatment outcomes. Through genetic profiling and biomarker analysis, physicians can identify patients who are most likely to respond to specific immunotherapies, optimizing treatment selection and improving overall patient care.
Benefits and Challenges of Immunotherapy
Improved survival rates and long-term responses:
One of the most significant benefits of immunotherapy is its ability to improve survival rates and achieve long-term responses in cancer patients. Unlike traditional treatments that often provide temporary relief, immunotherapy has shown remarkable durability in its effects. Patients who have undergone immunotherapy have experienced prolonged remission periods and, in some cases, even complete eradication of tumors. This extended survival and durable response highlight the immense potential of immunotherapy in offering long-lasting benefits to individuals fighting cancer.
Minimizing side effects compared to traditional treatments:
Immunotherapy has demonstrated a distinct advantage over traditional cancer treatments when it comes to minimizing side effects. While chemotherapy and radiation therapy often cause debilitating toxicities, immunotherapy works by stimulating the body’s immune system, resulting in more targeted and specific actions against cancer cells. As a result, many patients undergoing immunotherapy experience fewer adverse effects, such as nausea, hair loss, and fatigue, which are commonly associated with conventional treatments. This reduced toxicity not only improves patients’ quality of life during treatment but also allows them to better tolerate long-term therapy.
Challenges and limitations of immunotherapy:
- High costs and accessibility issues:
One major challenge associated with immunotherapy is its high costs, which can limit access for many patients. The development, production, and administration of immunotherapeutic agents involve intricate processes and advanced technologies, resulting in substantial treatment expenses. Additionally, certain immunotherapies require specialized facilities and expertise, which may not be readily available in all healthcare settings. Addressing these cost and accessibility barriers is crucial to ensuring that immunotherapy reaches a broader population and becomes a viable option for all eligible patients.
- Resistance and tumor escape mechanisms:
While immunotherapy has shown remarkable success, resistance to treatment can develop over time. Cancer cells can employ various mechanisms to evade immune system recognition, rendering immunotherapy less effective. Researchers are actively investigating strategies to overcome resistance, including combination therapies and novel immunotherapeutic targets. Understanding and addressing resistance mechanisms will be key to enhancing the long-term effectiveness of immunotherapy and maximizing patient outcomes.
- Autoimmune reactions and potential toxicities:
While immunotherapy is generally well-tolerated, it can lead to immune-related adverse events (irAEs) due to the activation of the immune system. These irAEs range from mild to severe and can affect various organs, including the skin, gastrointestinal tract, liver, and endocrine system. Monitoring and managing these toxicities require close collaboration between oncologists and immunotherapy specialists to ensure timely intervention and optimal patient care. Efforts are ongoing to develop strategies that balance treatment efficacy with minimizing potential toxicities.